HIPAA Violations Fines And Enforcement
| HIPAA Violation | Minimum Penalty | Maximum Penalty |
|---|---|---|
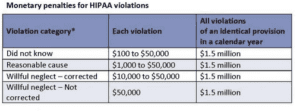
| Unknowing | $100 per violation, with an annual maximum of $25,000 for repeat violations (Note: maximum that can be imposed by State Attorneys General regardless of the type of violation) | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Reasonable Cause | $1,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $100,000 for repeat violations | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Willful neglect | $10,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $250,000 for repeat violations | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Willful neglect and not corrected | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million | $50,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $1.5 million |
HIPAA Violations Fines And Enforcement
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) enforces the HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules.
OCR enforces Privacy and Security Rules in several ways:
- Investigating complaints filed with it
- Conducting compliance reviews to determine if covered entities are in compliance
- Performing education and outreach to foster compliance with the rules’ requirements
OCR reviews the information that it gathers. In some cases, it may determine that the covered entity did not violate the Privacy and Security rules’ requirements. In the case of noncompliance, OCR will attempt to resolve the case with the covered entity by obtaining:
- Voluntary compliance
- Corrective action and
- Resolution agreement
Failure to comply with HIPAA can also result in civil and criminal penalties. If a complaint describes an action that could violate the unlawful provision of HIPAA, OCR may refer the complaint to the Department of Justice (DOJ) for investigation.
Civil Violations
In cases of noncompliance where the covered entity does not satisfactorily resolve the matter, OCR may decide to impose civil money penalties (CMPs) on the covered entity.
CMPs for HIPAA violations are determined based on a tiered civil penalty structure. The secretary of HHS has discretion in determining the penalty amount based on the nature and extent of the violation and the nature and extent of the harm resulting from the violation. The secretary is prohibited from imposing civil penalties (except in cases of willful neglect) if the violation is corrected within 30 days (this period may be extended at HHS’ discretion).
| HIPAA Violation | Minimum Penalty | Maximum Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Unknowing | $100 per violation, with an annual maximum of $25,000 for repeat violations (Note: maximum that can be imposed by State Attorneys General regardless of the type of violation) | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Reasonable Cause | $1,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $100,000 for repeat violations | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Willful neglect | $10,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $250,000 for repeat violations | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
| Willful neglect and not corrected | $50,000 per violation, with a yearly maximum of $1.5 million | $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million |
Criminal Penalties
The DOJ handles criminal violations of HIPAA. As with HIPAA civil penalties, there are different levels of severity for criminal violations.
As explained below, covered entities and specified individuals who “knowingly” obtain or disclose individually identifiable health information in violation of the Administrative Simplification Regulations face a fine of up to $50,000 and imprisonment of up to 1 year.
Offenses committed under pretenses allow penalties to be increased to a $100,000 fine, with up to 5 years in prison.
Finally, offenses committed intending to sell, transfer, or use individually identifiable health information for commercial advantage, personal gain, or malicious harm permit fines of $250,000 and imprisonment of up to 10 years.
Covered Entities
Criminal penalties for HIPAA violations are directly applicable to covered entities (CE), including:
- Health plans
- Health care clearinghouses
- Healthcare providers who transmit claims in electronic form
- Medicare prescription drug card sponsors
Individuals such as the CE’s directors, employees, or officers (where the CE is not an individual) may also be directly criminally liable under HIPAA per “corporate criminal liability.” Where an individual of a CE is not directly accountable under HIPAA, they can still be charged with conspiracy or aiding and abetting.
Unpacking HIPAA Violations: What You Need to Know About Fines and How to Stay Compliant
Are you a healthcare provider or a business handling sensitive patient information? If so, you must be well-versed in HIPAA regulations to protect your organization from fines. This article will unpack HIPAA violations, shed light on potential penalties, and provide essential tips to keep your operations compliant.
HIPAA, which stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets the standards for safeguarding protected health information (PHI). Violating these regulations can result in severe penalties that can put your organization at significant financial risk.
Understanding the different types of HIPAA violations and the associated fines is critical to ensuring your compliance efforts are up to par. From unauthorized disclosures to failing to conduct risk assessments, we will explore the common reasons organizations find themselves in violation.
Additionally, we will share practical strategies to help you comply with HIPAA regulations. You can safeguard your patients’ data and avoid costly penalties by implementing proper training, adopting secure technologies, and conducting regular audits.
Stay tuned to learn everything you need to know about HIPAA violations, fines, and how to maintain compliance in today’s digital age.
What is HIPAA, and why is it important?
HIPAA, which stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets the standards for safeguarding protected health information (PHI). It was enacted in 1996 to establish guidelines for securing and transmitting personal health information. HIPAA is crucial because it ensures the privacy and security of patients’ sensitive data, promotes the electronic exchange of health information and enables individuals to have greater control over their healthcare information.
Organizations must implement administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to comply with HIPAA regulations to protect PHI. This includes implementing policies and procedures, training employees, securing electronic systems, and conducting regular risk assessments.
Common HIPAA violations and their consequences
Understanding the different types of HIPAA violations and the associated fines is critical to ensuring your compliance efforts are up to par. Violations can occur in various forms, including unauthorized disclosures, inadequate safeguards, lack of training, and failure to conduct risk assessments. Let’s look closely at some common violations and their potential consequences.
1. Unauthorized Disclosures: This occurs when PHI is shared without proper authorization from the patient. This can happen through accidental breaches, such as sending an email with sensitive information to the wrong recipient, or intentional breaches, such as sharing patient information without valid consent. Unauthorized disclosures can lead to reputational damage, loss of trust, and significant financial penalties.
2. Inadequate Safeguards: HIPAA requires organizations to implement appropriate security measures to protect PHI. Failure to do so can result in severe consequences. For example, if a healthcare provider does not have proper encryption in place and experiences a data breach, they can face substantial fines, legal actions, and damage to their reputation.
3. Lack of Training: HIPAA mandates that all employees receive training on privacy and security practices. Failure to provide adequate training can result in accidental or intentional violations. For instance, an improperly trained employee may inadvertently disclose patient information to unauthorized individuals, leading to potential breaches and penalties.
4. Failure to Conduct Risk Assessments: HIPAA requires organizations to conduct regular risk assessments to identify system and process vulnerabilities. Failing to perform these assessments can leave organizations unaware of potential security risks and increase the likelihood of violations. In a breach, the organization may face higher penalties due to negligence.
HIPAA fines and penalties
Violating HIPAA regulations can result in severe penalties that can put your organization at significant financial risk. The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) enforces HIPAA compliance. It can impose fines based on the severity of the violation. Let’s explore the potential fines and penalties associated with HIPAA violations.
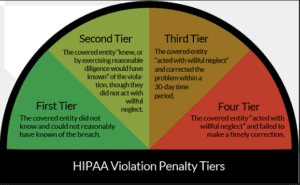
1. Tier 1: The lowest level of penalties applies when the organization was unaware of the violation and would not have known even with reasonable diligence. Fines range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million.
2. Tier 2: This level applies when the organization is aware of the violation but does not act with willful neglect. Fines range from $1,000 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million.
3. Tier 3: The highest penalties apply when the organization acted with willful neglect and failed to correct the violation within a reasonable timeframe. Fines range from $10,000 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million.
In addition to financial penalties, organizations that violate HIPAA regulations may face criminal charges, civil lawsuits, and reputational damage. The consequences can be severe, making it imperative for healthcare providers and businesses to prioritize HIPAA compliance.
Steps to take after a HIPAA violation
Discovering a HIPAA violation can be overwhelming, but immediate action is essential to mitigate the potential damages. Here are some crucial steps to follow if your organization experiences a HIPAA violation:
1. Identify and Contain the Breach: Determine the extent of the violation and take immediate steps to contain it. This may involve isolating affected systems, restricting access, and alerting the appropriate individuals.
2. Assess the Impact: Evaluate the potential risks and harms resulting from the breach. This includes determining the type and amount of PHI involved, the likelihood of damage to individuals, and the possible reputational and financial consequences.
3. Notify Affected Individuals: HIPAA requires organizations to notify individuals affected by a breach. Provide clear and concise information about the incident, the steps to address it, and any protective measures individuals can take.
4. Report to the Appropriate Authorities: In certain situations, organizations must report the breach to the OCR, state agencies, or other regulatory bodies. Familiarize yourself with the reporting requirements to ensure compliance.
5. Conduct a Thorough Investigation: Investigate the cause of the breach and identify any vulnerabilities in your systems or processes. This will help prevent similar incidents and demonstrate your commitment to resolving the issue.
6. Implement Corrective Actions: Take steps to address the root cause of the violation and prevent future occurrences. This may involve updating policies and procedures, enhancing employee training, and implementing additional security measures.
7. Learn from the Experience: Use the breach to improve your organization’s security posture. Regularly review and update your HIPAA compliance program, stay informed about industry best practices, and continuously educate your staff.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage a HIPAA violation and minimize the potential damages to your organization.
How to prevent HIPAA violations in your organization
Prevention is always better than dealing with the aftermath of a HIPAA violation. Here are some practical strategies to help you stay compliant with HIPAA regulations and protect your organization from penalties:
1. HIPAA Compliance Training and Education: Ensure all employees receive comprehensive training on HIPAA regulations, privacy practices, and security protocols. Regularly update training materials to reflect any rules or changes in industry standards.
2. HIPAA-Compliant Technology Solutions: Implement secure technologies that encrypt data, protect against unauthorized access, and enable secure communication and storage of PHI. This may include secure email systems, encrypted file-sharing platforms, and robust firewalls.
3. The Role of Risk Assessments in HIPAA Compliance: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and gaps in your systems and processes. This proactive approach allows you to address potential risks before they result in violations.
4. Strict Access Controls: Implement strong access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can access PHI. This includes unique user IDs, passwords, two-factor authentication, and regular access reviews.
5. Employee Accountability: Hold employees accountable for their actions by establishing clear policies and procedures, enforcing consequences for violations, and regularly auditing their compliance with HIPAA regulations.
6. Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take during a breach. This will help your organization respond quickly and effectively, minimizing the potential damages.
7. Regular Audits and Monitoring: Conduct regular internal audits and monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance with HIPAA regulations. This includes reviewing access logs, monitoring system activity, and addressing identified vulnerabilities.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a culture of compliance within your organization and reduce the risk of HIPAA violations.
HIPAA compliance training and education
To better understand the real-world impact of HIPAA violations, let’s explore a few notable case studies:
1. Anthem Inc. Data Breach: In 2015, Anthem Inc., one of the largest health insurance companies in the United States, experienced a massive data breach affecting nearly 78.8 million individuals. The breach occurred due to a phishing email sent to an employee, allowing hackers to access sensitive data. Anthem Inc. settled the case for $115 million, one of the largest settlements in HIPAA history.
2. Cottage Health System Breach: In 2013, Cottage Health System, a California-based healthcare provider, suffered a data breach that exposed the personal information of approximately 55,000 patients. The breach occurred due to the lack of appropriate security measures, including the failure to implement encryption. Cottage Health System settled the case for $2 million.
These case studies highlight the significant financial consequences and reputational damage organizations can face due to HIPAA violations. It serves as a reminder of the importance of prioritizing HIPAA compliance to protect patient data and avoid costly penalties.
HIPAA-compliant technology solutions
Maintaining HIPAA compliance is crucial for healthcare providers and businesses handling sensitive patient information. Violating HIPAA regulations can result in severe penalties, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Organizations can protect themselves and their patients’ data by understanding the common HIPAA violations and the associated fines and implementing preventive measures.
Remember to prioritize employee training, adopt secure technologies, conduct regular risk assessments, and respond promptly and effectively in the event of a breach. By doing so, you can navigate the complex landscape of HIPAA regulations and ensure the privacy and security of patient information in today’s digital age. Stay compliant, stay secure, and safeguard the trust of those you serve.
The role of risk assessments in HIPAA compliance
When safeguarding protected health information (PHI), using HIPAA-compliant technology solutions is crucial. These solutions are designed to meet HIPAA’s strict security and privacy requirements. By leveraging these tools, healthcare providers and businesses can ensure that patient data remains secure and compliant.
One such technology solution is encrypted messaging platforms. These platforms allow healthcare professionals to securely communicate and share patient information without risking unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that the data remains protected, even if it falls into the wrong hands.
Another essential technology solution is a secure patient portal. This online platform allows patients to access their health records, schedule appointments, and communicate with healthcare providers securely. Organizations can streamline workflows by implementing a patient portal while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
Furthermore, cloud storage solutions that meet HIPAA requirements provide a secure way to store and access patient data. These solutions typically offer encryption, access controls, and regular backups to protect against data breaches or loss.
By investing in HIPAA-compliant technology solutions, healthcare providers and businesses can enhance their security measures and reduce the risk of HIPAA violations. It is essential to thoroughly research and select solutions that align with your organization’s specific needs and requirements.
HIPAA violation case studies
Conducting regular risk assessments is a critical aspect of maintaining HIPAA compliance. Risk assessments help organizations identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their systems, processes, and policies that could lead to HIPAA violations.
During a risk assessment, organizations evaluate their security measures and identify gaps or areas for improvement. This includes assessing physical security, technical safeguards, administrative controls, and employee training programs.
Physical security measures involve securing physical access to areas where patient information is stored or processed. This can include installing surveillance cameras, implementing access control systems, and properly disposing of physical records.
Technical safeguards encompass security measures that protect electronic PHI. This includes implementing firewalls, encryption, secure login credentials, and regular software updates to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Administrative controls involve establishing policies and procedures for handling patient information. This includes training employees on HIPAA regulations, creating incident response plans, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance.
Employee training is a crucial component of HIPAA compliance. Educating employees about their responsibilities in safeguarding patient information, recognizing potential security threats, and following proper procedures for handling PHI is essential.
By conducting regular risk assessments and addressing identified vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively mitigate the risk of HIPAA violations and demonstrate their commitment to patient privacy and security.
10: Conclusion
Let’s delve into some real-life case studies to understand better the consequences of HIPAA violations and the associated fines. These examples highlight common scenarios where organizations have failed to comply with HIPAA regulations, resulting in significant penalties.
Case Study 1: ABC Healthcare
ABC Healthcare, an extensive hospital network, experienced a data breach when an employee fell victim to a phishing scam. The hacker accessed the hospital’s system, compromising the PHI of thousands of patients. The breach resulted from the employee failing to promptly recognize and report the phishing attempt.
As a result of the breach, ABC Healthcare faced a fine of $4.3 million. The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) determined that the hospital had failed to implement adequate security measures and provide proper employee training to prevent such incidents. The fine served as a reminder of the importance of robust cybersecurity practices and ongoing training.
Case Study 2: XYZ Medical Clinic
XYZ Medical Clinic, a small healthcare facility, faced severe penalties due to multiple HIPAA violations. The clinic failed to conduct regular risk assessments, lacked proper encryption measures, and did not have a breach notification process. These violations came to light when a former employee reported the clinic’s noncompliance with the OCR.
As a result, XYZ Medical Clinic was hit with a fine of $2.5 million. The OCR found that the clinic had neglected its responsibilities to protect patient information, putting the privacy and security of thousands of individuals at risk. This case emphasizes the importance of regular compliance audits and the need for comprehensive policies and procedures.
These case studies demonstrate the significant financial impact of HIPAA violations. Healthcare providers and businesses must prioritize compliance efforts and invest in robust security measures to avoid costly penalties.
Interpreting “Knowingly”
The DOJ interpreted the “knowingly” element of the HIPAA statute for criminal liability as requiring only knowledge of the actions that constitute an offense. Specific knowledge of an act violating the HIPAA statute is not required.
Exclusion From Medicare
HHS has the authority to exclude from participation in Medicare any CE that was not compliant with the transaction and code set standards by Oct. 16, 2003 (where an extension was obtained, and the CE is not small) (68 FR 48805).
Article link:
https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/hipaa-violations-enforcement

